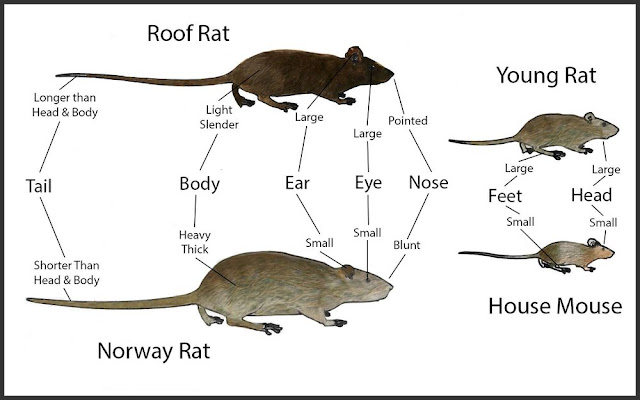
A successful
rat control strategy typically includes three elements: sanitation measures; building construction and rodent proofing; and, if necessary, population control.
SanitationSanitation is fundamental to rat control and must be continuous. If sanitation measures aren’t properly maintained, the benefits of other measures will be lost and rats will quickly return. Good housekeeping in and around buildings will reduce available shelter and food sources for Norway rats and, to some extent, roof rats. Neat, off-the-ground storage of pipes, lumber, firewood, crates, boxes, gardening equipment, and other household goods will help reduce the suitability of the area for rats and also will make their detection easier. Collect garbage, trash, and garden debris frequently, and ensure all garbage receptacles have tight-fitting covers. Where dogs are kept and fed outdoors, rats can become a problem if there is a ready supply of dog food. Feed your pet only the amount of food it will eat at a feeding, and store pet food in rodent-proof containers.
![Rats Control Rats Control]()
For roof rats in particular, thinning dense vegetation will make the habitat less desirable. Climbing hedges such as Algerian or English ivy, star jasmine, and honeysuckle on fences or buildings are conducive to roof
rat infestations and should be thinned or removed if possible, as should overhanging tree limbs within 3 feet of the roof. Separate the canopy of densely growing plants such as pyracantha and juniper from one another and from buildings by a distance of 2 feet or more to make it more difficult for rats to move between them.
Building Construction and Rodent ProofingThe most successful and long-lasting form of rat control in structures is exclusion, or “building them out.” (See Rodent-proofing your home.) Seal cracks and openings in building foundations and any openings for water pipes, electric wires, sewer pipes, drain spouts, and vents. No hole larger than 1/4 inch should be left unsealed, in order to exclude both rats and house mice. Make sure doors, windows, and screens fit tightly. Their edges can be covered with sheet metal if gnawing is a problem. Coarse steel wool, wire screen, and lightweight sheet metal are excellent materials for plugging gaps and holes. Norway and roof rats are likely to gnaw away plastic sheeting, wood, caulking, and other less sturdy materials.
Because rats and house mice are excellent climbers, openings above ground level must also be plugged. Rodent proofing against roof rats, because of their greater climbing ability, usually requires more time to find entry points than for Norway rats. Roof rats often enter buildings at the roofline, so be sure that all access points in the roof are sealed. If roof rats are traveling on overhead utility wires, contact a pest control professional or the utility company for information and assistance with measures that can be taken to prevent this.
Population ControlWhen food, water, and shelter are available, rat populations can increase quickly. While the most permanent form of control is to limit food, water, shelter, and access to buildings, direct population control often is necessary.
For controlling rats indoors, using traps is best. When rodenticides (toxic baits) are used in structures, rats can die in inaccessible locations such as within walls or ceilings. In hot weather, the stench of a dead rat can be unbearable and can necessitate cutting a hole in the wall to remove the carcass. Also, ectoparasites such as fleas and mites often leave dead rat carcasses and can infest the entire house if the carcass isn’t removed promptly.
TrappingTrapping is the safest and most effective method for controlling rats in and around homes, garages, and other structures. Because snap traps can be used over and over, trapping is less costly than poison baits but more labor intensive. Traps can be set and left indefinitely in areas such as attics where rats have been a problem in the past. The simple, wooden rat-size snap trap is the least expensive option, but some people prefer the newer plastic, single-kill rat traps, because they are easier to set and to clean. Snap traps with large plastic treadles are especially effective, but finding the best locations to set traps is often more important than what type of trap is used. Generally, young rats can’t be trapped until they are about a month old, which is when they leave the nest to venture out for food.
Nutmeats, dried fruit, bacon, or a piece of kibbled pet food can be an attractive bait for traps. Fasten the bait securely to the trigger of the trap with light string, thread, or fine wire so the rodent will spring the trap when attempting to remove the food. Even glue can be used to secure the bait to the trigger. Soft baits such as peanut butter and cheese can be used, but rats sometimes take soft baits without setting off the trap. Set traps so the trigger is sensitive and will spring easily.
The best places to set traps are in secluded areas where rats are likely to travel and seek shelter. Droppings, gnawings, and damage indicate the presence of rodents, and areas where such evidence is found usually are the best places to set traps, especially when these areas are located between their shelter and food sources. Place traps in natural travel ways, such as along walls, so the rodents will pass directly over the trigger of the trap.
Full Article
Here